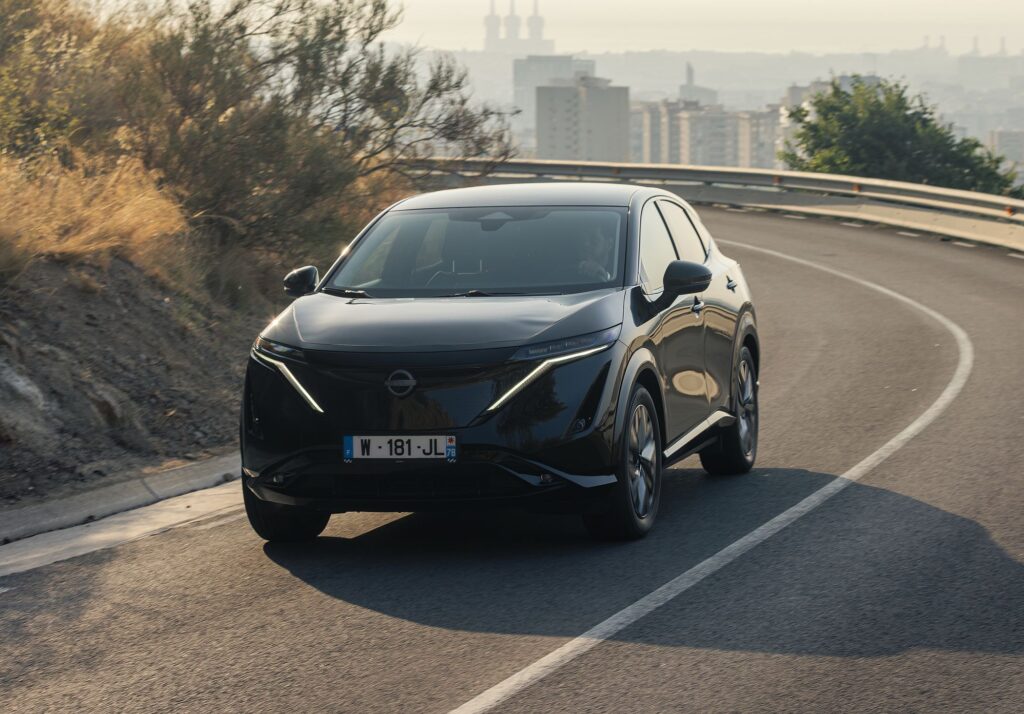
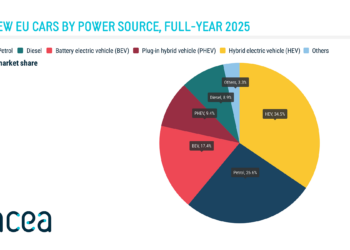
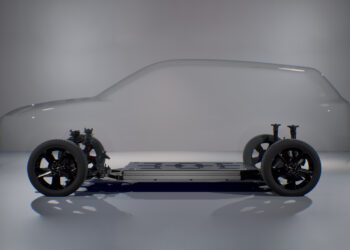
Nissan has introduced a special project based on the Ariya, which allows the use of solar panels to extend the range of the 100% electric SUV by up to 23 km/day, provided that the weather conditions are ideal. This prototype, revealed on International Clean Energy Day, January 26, explores the potential of a technology capable of enhancing the capabilities of vehicles with electric drivetrains.
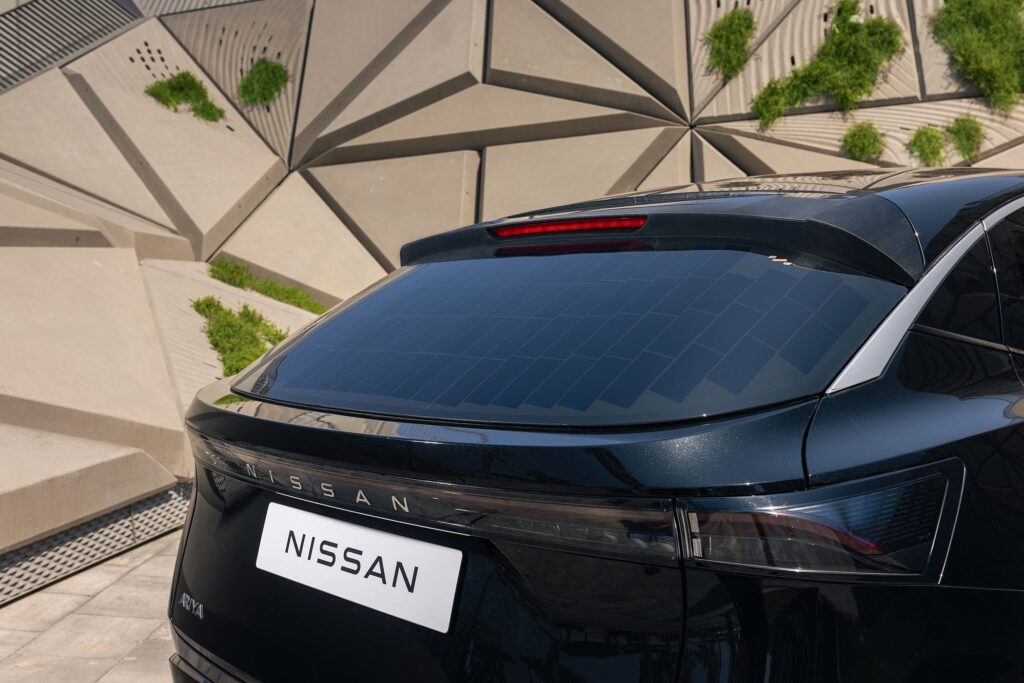
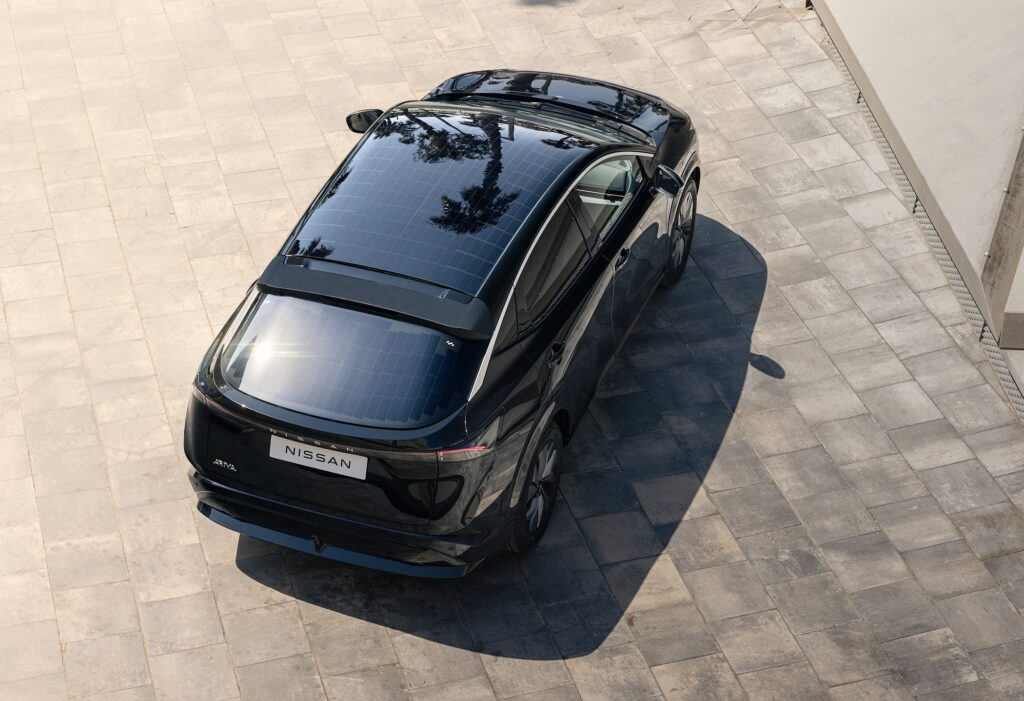
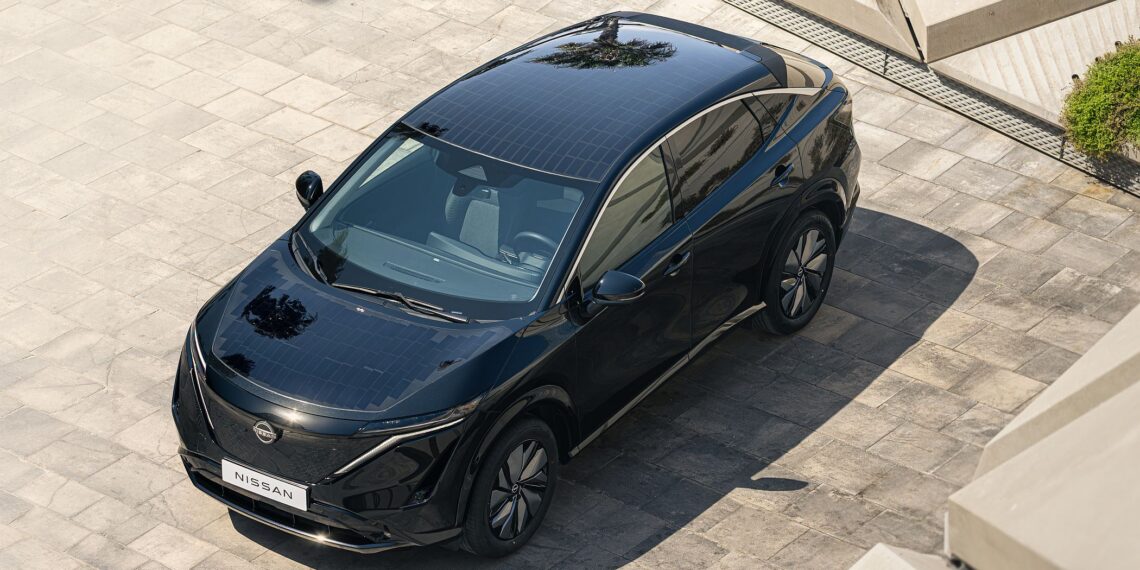
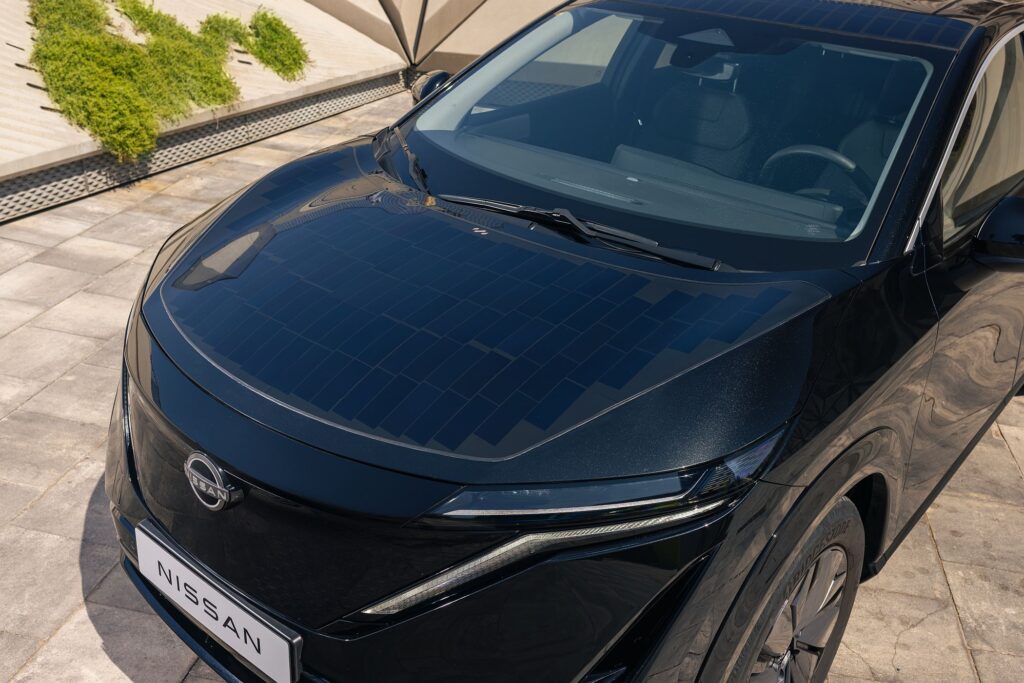
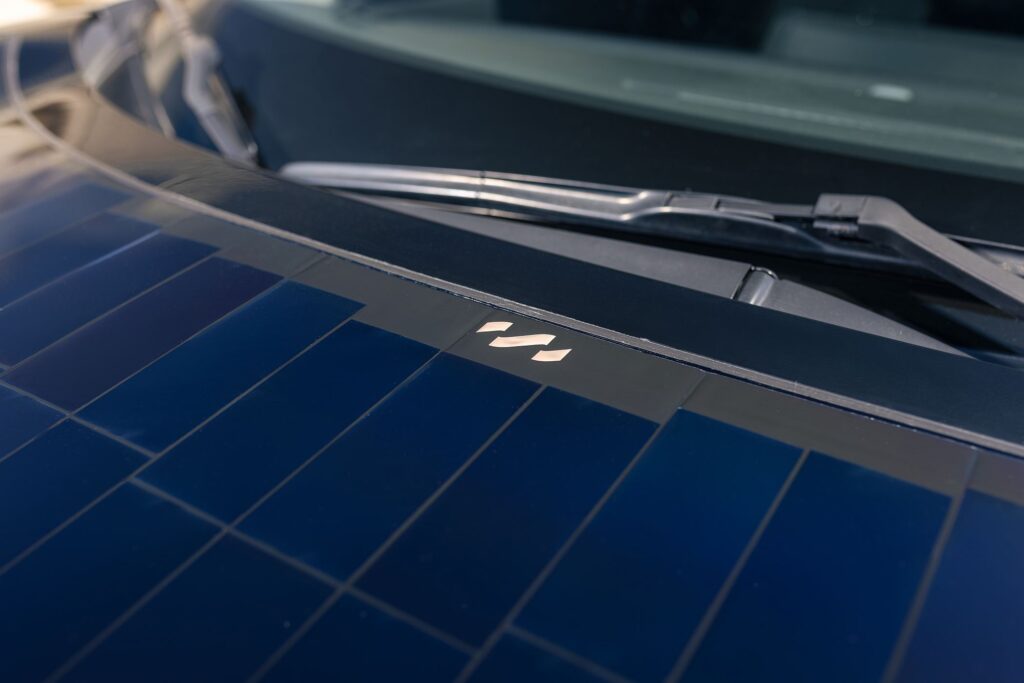
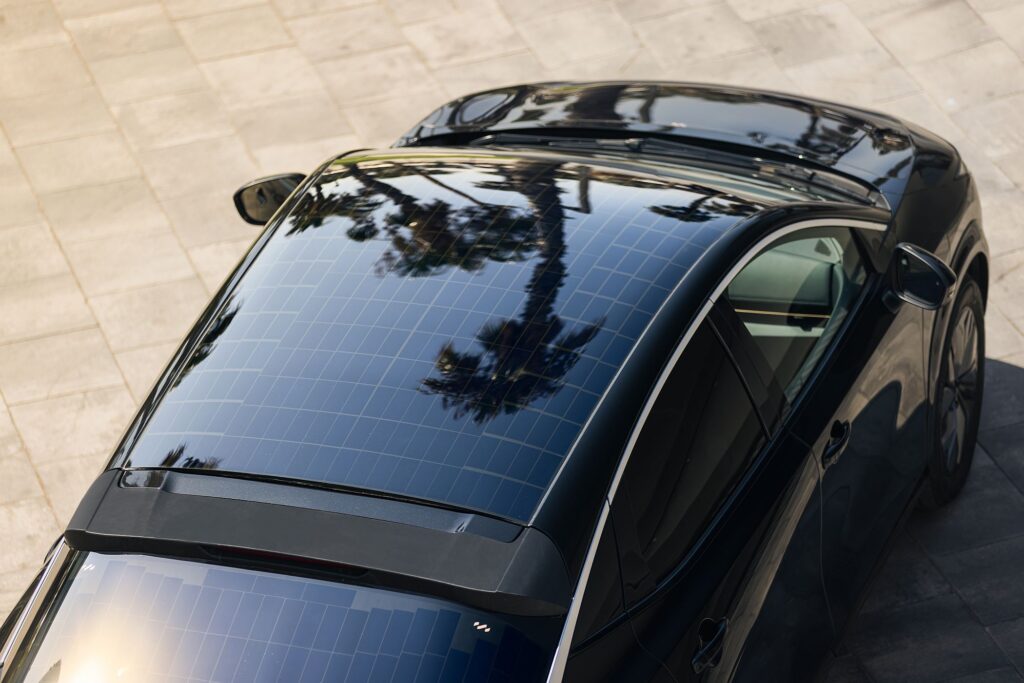
A result of collaboration between the engineers from Nissan’s Advanced Product Planning in Dubai and the Powertrain Planning team in Barcelona, this Ariya features 3.8 m2 of photovoltaic panels integrated into the “hood,” roof, and rear gate. The equipment was developed in collaboration with Lightyear, a Dutch company specializing in solar mobility.
The solar panels, made with polymers and glass, convert sunlight into direct current (DC), managed by an advanced controller designed to optimize energy use and reduce dependence on external battery charging infrastructures. Under ideal conditions, this equipment ensures an additional range of up to 23 km per day, although this figure always depends on solar exposure conditions: in sunnier cities like Barcelona, the vehicle can achieve an average of up to 17.6 km, with the distance increasing to up to 21.2 km in Dubai. In other cities, such as London in the UK, it adds only an additional 10.2 km/day.




According to Nissan, with this equipment, drivers can reduce the frequency of charging by 35%-65%, depending on the use of the vehicle. On a two-hour trip, or 80 km, an additional 0.5 kWh of clean energy can be produced, adding up to 3 km to the SUV’s range. In regions with limitations regarding charging networks, this will be a technology with many benefits.
The first long-distance tests, which included a trip of 1550 km between the Netherlands and Barcelona, demonstrated that the integration of solar panels would be able to reduce annual visits to charging stations from 23 to 8, in the case of a driver who travels only 6000 km/year.